Lincoln Corsair: Power Steering / Diagnosis and Testing - Power Steering
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Chart
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
| Module | DTC | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | C0051:23 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Stuck Low | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:27 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Rate Of Change Above Threshold | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:28 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out Of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:29 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Invalid | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:54 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Missing Calibration | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:62 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Compare Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:64 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:67 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Incorrect After Event | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:82 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Alive/Sequence Counter Incorrect/Not Updated | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:85 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Above Allowable Range | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:86 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Invalid | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C0051:96 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Component Internal Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| ABS | C006B:00 | Stability System Active Too Long: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| PSCM | B1D23:4B | Overheat Sensor: Over Temperature | GO to Pinpoint Test BB |
| PSCM | C1110:56 | Power steering Calibration Data: Invalid/Incompatible Configuration | GO to Pinpoint Test AA |
| PSCM | C1B00:49 | Steering Angle Sensor: Internal Electronic Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BF |
| PSCM | C1B00:62 | Steering Angle Sensor: Signal Compare Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BF |
| PSCM | C200B:49 | Steering Shaft Torque Sensor 1: Internal Electronic Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BG |
| PSCM | C200B:62 | Steering Shaft Torque Sensor 1: Signal Compare Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BG |
| PSCM | C200D:49 | Motor Rotation Angle Sensor: Internal Electronic Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BI |
| PSCM | C200D:62 | Motor Rotation Angle Sensor: Signal Compare Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BI |
| PSCM | U0100:00 | Lost Communication With ECM/PCM 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AJ |
| PSCM | U0121:00 | Lost Communication With Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AK |
| PSCM | U0140:00 | Lost Communication With Body Control Module: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AL |
| PSCM | U0146:00 | Lost Communication With Serial Data Gateway 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AM |
| PSCM | U0151:00 | Lost Communication With Restraints Control Module: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AN |
| PSCM | U0155:00 | Lost Communication With Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) Control Module: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AO |
| PSCM | U0159:00 | Lost Communication With Parking Assist Control Module 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AP |
| PSCM | U0212:00 | Lost Communication With Steering Column Control Module: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AQ |
| PSCM | U023A:00 | Lost Communication With Image Processing Module A: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AR |
| PSCM | U0401:00 | Invalid Data Received from ECM/PCM A: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AS |
| PSCM | U0415:00 | Invalid Data Received from Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AT |
| PSCM | U0415:22 | Invalid Data Received from Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module 'A': Signal Amplitude Greater Than Maximum | GO to Pinpoint Test AT |
| PSCM | U0429:00 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Column Control Module: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AU |
| PSCM | U0447:00 | Invalid Data Received From Serial Data Gateway 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AV |
| PSCM | U045A:00 | Invalid Data Received From Parking Assist Control Module 'A': No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AW |
| PSCM | U053B:00 | Invalid Data Received From Image Processing Module A: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test AX |
| PSCM | U2016:09 | Control Module Main Software: Component Failures | GO to Pinpoint Test BO |
| PSCM | U2016:47 | Control Module Main Software: Watchdog/Safety µC Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BO |
| PSCM | U2016:48 | Control Module Main Software: Supervision Software Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test BO |
| PSCM | U2016:57 | Control Module Main Software: Invalid/Incompatible Software Component | GO to Pinpoint Test BO |
| PSCM | U2016:66 | Control Module Main Software: Signal Has Too Many Transitions/Events | GO to Pinpoint Test BO |
| PSCM | U2016:94 | Control Module Main Software: Unexpected Operation | GO to Pinpoint Test BO |
| PSCM | U2100:00 | Initial Configuration Not Complete: No Sub Type Information | GO to Pinpoint Test BQ |
| PSCM | U2300:55 | Central Configuration: Not Configured | GO to Pinpoint Test AB |
| PSCM | U3000:05 | Control Module: System Programming Failures | GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| PSCM | U3000:42 | Control Module: General Memory Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| PSCM | U3000:49 | Control Module: Internal Electronic Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| PSCM | U3000:4B | Control Module: Over Temperature | GO to Pinpoint Test BE |
| PSCM | U3000:61 | Control Module: Signal Calculation Failure | GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| PSCM | U3000:66 | Control Module: Signal Has Too Many Transitions/Events | GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| PSCM | U3001:68 | Control Module Improper Shutdown Performance: Event Information | GO to Pinpoint Test BD |
| PSCM | U3003:16 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Below Threshold | GO to Pinpoint Test BC |
| PSCM | U3003:17 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Above Threshold | GO to Pinpoint Test BC |
| PSCM | U3003:68 | Battery Voltage: Event Information | GO to Pinpoint Test BC |
Global Customer Symptom Code (GCSC) Chart
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Steering/Steering Wheel > Feel/Wander/Pull > Intermittent | GO to Pinpoint Test D |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Steering/Steering Wheel > Performance > Intermittent | GO to Pinpoint Test D |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Fluids > Steering > Visible Leak | GO to Pinpoint Test BA |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Stopping > High Speed | GO to Pinpoint Test AI |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Stopping > Low Speed | GO to Pinpoint Test AF |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Stopping > Low Speed | GO to Pinpoint Test AI |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Steering > Intermittent | GO to Pinpoint Test AF |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Steering > Over Bump | GO to Pinpoint Test AC |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Steering > Low Speed | GO to Pinpoint Test AE |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Steering > While Turning | GO to Pinpoint Test AD |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Steering > While Turning | GO to Pinpoint Test AE |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Front > Over Bump | GO to Pinpoint Test AC |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Noise > Front > Low Speed | GO to Pinpoint Test AF |
| Stop/Steer/Ride > Vibration > Steering > Intermittent | GO to Pinpoint Test E |
Symptom Chart(s)
Symptom Chart: Steering System and NVH
-
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
-
NVH
symptoms should be identified using the diagnostic tools available.
For a list of these tools, an explanation of their uses and a glossary
of common terms,
REFER to: Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH) (100-04 Noise, Vibration and Harshness, Description and Operation).
. Since it is possible any one of multiple systems may be the cause of a symptom, it may be necessary to use a process of elimination type diagnostic approach to pinpoint the responsible system. If this is not the causal system for the symptom, REFER to: Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH) (100-04 Noise, Vibration and Harshness, Description and Operation).
for the next likely system and continue diagnostics. - If equipped, the Lane Keeping System (LKS) can interfere with accurate EPAS diagnostics. Disable the Lane Keeping System (LKS) before test driving the vehicle to diagnose EPAS concerns. For information on disabling the Lane Keeping System (LKS), refer to Owner's Literature.
There are multiple conditions (overheating protection, high voltage, low voltage, etc.) which result in limited or reduced assist from the EPAS system. Address all existing PSCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) prior to diagnosing any assist symptoms.
| Condition | Actions |
|---|---|
| Message center displays STEERING FAULT SERVICE NOW | GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| Message center displays STEERING ASSIST FAULT SERVICE REQUIRED | GO to Pinpoint Test J |
| Message center displays STEERING LOSS STOP SAFELY | GO to Pinpoint Test Z |
| ABS Module DTC C0051:XX Steering Angle Concerns With The PSCM | GO to Pinpoint Test AG |
| DTC U0131:XX A module cannot communicate with the PSCM | GO to Pinpoint Test C |
| DTC U0420:XX Invalid Data Received From The PSCM | GO to Pinpoint Test BL |
| The PSCM cannot communicate with the diagnostic scan tool | GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| ASSIST - Open PSCM Fuse(s) | GO to Pinpoint Test A |
| ASSIST - Unable to replicate customers intermittent assist concern during a test drive | GO to Pinpoint Test F |
| LEAKING - Steering gear appears to be leaking fluid | GO to Pinpoint Test BA |
| NOISE - During acceleration (tip in) or deceleration (tip out) may occur with braking | GO to Pinpoint Test AF |
| NOISE - During braking | GO to Pinpoint Test AI |
| NOISE - Driving straight on smooth roads | GO to Pinpoint Test L |
| NOISE - Over bumps, rough roads, dips, depressions or when entering a driveway | GO to Pinpoint Test AC |
| NOISE - Turning at slow speeds or during parking lot maneuvers | GO to Pinpoint Test AE |
| NOISE - noticed more in the interior | GO to Pinpoint Test AD |
| STEERING - Excessive steering wheel play | GO to Pinpoint Test R |
| STEERING - Lack of assist or inconsistent assist | GO to Pinpoint Test BK |
| STEERING - Poor returnability or sticky steering or binding | GO to Pinpoint Test I |
| STEERING - Steering system pull, drift or wander | GO to Pinpoint Test H |
| STEERING WHEEL - Steering wheel is off center | GO to Pinpoint Test BC |
Pinpoint Tests
 PINPOINT TEST A: OPEN PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
FUSE(S)
PINPOINT TEST A: OPEN PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
FUSE(S)|
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions There are 2 power sources for the PSCM , the high current power steering fuse, and the low current power steering fuse. Refer to the wiring diagrams to review the PSCM circuit for both the high current and low current fuse locations as well as the associated power and ground wiring. Open power steering fuse can occur when the power or ground wiring is shorted against another component or water intrusion in the respective connectors or connections. Possible Sources
|
 COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE |
|
 PINPOINT TEST B:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U3000 CONTROL MODULE
PINPOINT TEST B:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U3000 CONTROL MODULE
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST C:
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0131:XX A MODULE CANNOT COMMUNICATE WITH THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
PINPOINT TEST C:
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0131:XX A MODULE CANNOT COMMUNICATE WITH THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
|
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE |
|
 PINPOINT TEST D: UNABLE TO REPLICATE CUSTOMERS INTERMITTENT ASSIST CONCERN DURING A TEST DRIVE
PINPOINT TEST D: UNABLE TO REPLICATE CUSTOMERS INTERMITTENT ASSIST CONCERN DURING A TEST DRIVE|
NOTE: Customers may report an intermittent power steering concern that may not replicate during a test drive session. TSB , SSM or Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) may exist indicating the likely root cause. Retrieve all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) for the vehicle, as well as TSB , SSM . Normal Operation and Fault Conditions there are 2 power sources for the PSCM , the high current power steering fuse, and the low current power steering fuse. Refer to the wiring diagrams to review the PSCM circuit for both the high current and low current fuse locations as well as the associated power and ground wiring. Open power steering fuse can occur when the power or ground wiring is shorted against another component or water intrusion in the respective connectors or connections.
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Possible Sources
|
||||
| D1 CHECK THE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM ALL MODULES | ||||
Are Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the PSCM or any other modules?
|
 PINPOINT TEST E: STEERING WHEEL VIBRATES OR RESISTS TURNING
PINPOINT TEST E: STEERING WHEEL VIBRATES OR RESISTS TURNING|
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Description
Description
REFER to: Lane Keeping System - System Operation and Component
Description (419-07 Lane Keeping System, Description and Operation).
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability This test DOES NOT apply to any other DTC or symptom. Diagnostic Strategy
Diagnostic Strategy
Possible Sources
|
| Diagnostic steps are not provided for this symptom or DTC. REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). |
 PINPOINT TEST F: UNABLE TO REPLICATE CUSTOMERS INTERMITTENT ASSIST CONCERN DURING A TEST DRIVE
PINPOINT TEST F: UNABLE TO REPLICATE CUSTOMERS INTERMITTENT ASSIST CONCERN DURING A TEST DRIVE|
NOTE: Customers may report an intermittent power steering concern that may not replicate during a test drive session. TSB , SSM or Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) may exist indicating the likely root cause. Retrieve all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) for the vehicle, as well as TSB , SSM . Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions there are 2 power sources for the PSCM , the high current power steering fuse, and the low current power steering fuse. Refer to the wiring diagrams to review the PSCM circuit for both the high current and low current fuse locations as well as the associated power and ground wiring. Open power steering fuse can occur when the power or ground wiring is shorted against another component or water intrusion in the respective connectors or connections. Possible Sources
|
 COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE |
|
 PINPOINT TEST G: THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
CANNOT COMMUNICATE WITH THE DIAGNOSTIC SCAN TOOL
PINPOINT TEST G: THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
CANNOT COMMUNICATE WITH THE DIAGNOSTIC SCAN TOOL|
Possible Sources
|
 COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE COMPLETE THE FDRS GUIDED ROUTINE |
|
 PINPOINT TEST H: STEERING WHEEL IS OFF CENTER, STEERING SYSTEM PULL, DRIFT OR WANDER
PINPOINT TEST H: STEERING WHEEL IS OFF CENTER, STEERING SYSTEM PULL, DRIFT OR WANDER
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). The EPAS system is designed to compensate for some steering issues (drift, pull, wander, etc.). However, if the steering issue is severe enough, the condition or symptom may become noticeable to the driver. The system starts compensating when vehicle speed exceeds 40 km/h (25 mph) and the vehicle is traveling straight. The system compensates on any road crown condition; however, some amount of pull is present during, and shortly after, quick lane transitions. After driving straight on a constant road crown with both hands on the steering wheel for at least 45 seconds, the pull condition can be assessed. The system does not compensate when turning at low speeds. For the system to compensate, the driver's hands must remain on the steering wheel. Drift describes what a vehicle with this condition does with the hands off the steering wheel. A vehicle-related drift, on a flat road, can cause a consistent deviation from the straight-ahead path and require constant steering input in the opposite direction to counteract the effect. Drift can be induced by conditions external to the vehicle, such as wind or road camber. Pull is described as a tugging sensation on the steering wheel felt by the driver, which must be overcome to keep the vehicle going straight. Wander is the tendency of the vehicle to require frequent, random left and right steering wheel corrections to maintain a straight path down a level road. Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST I: POOR RETURNABILITY OR STICKY STEERING
PINPOINT TEST I: POOR RETURNABILITY OR STICKY STEERING
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). With a fully charged battery and the ignition ON, the EPAS system provides adequate assist to maneuver the vehicle and return to the straight-ahead position with little difficulty. The assist provided by the EPAS system should be smooth and consistent at all times. The steering and suspension components should be free of any binding conditions and should not interfere with the steering assist provided by the EPAS system. If the steering wheel is held at the end of travel for more than 2 seconds, the level of assistance is noticeably reduced by the EPAS system. This is a normal condition programmed into the PSCM to protect the system from permanent damage. Poor returnability or sticky steering is used to describe the poor return of the steering wheel to center after a turn or steering correction is completed. Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST J: MESSAGE CENTER DISPLAYS STEERING ASSIST FAULT SERVICE REQUIRED
PINPOINT TEST J: MESSAGE CENTER DISPLAYS STEERING ASSIST FAULT SERVICE REQUIRED|
NOTE:
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Possible Sources |
| Diagnostic steps are not provided for this symptom or DTC. REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). |
 PINPOINT TEST L: FRONT END NOISE - DRIVING STRAIGHT ON SMOOTH ROADS
PINPOINT TEST L: FRONT END NOISE - DRIVING STRAIGHT ON SMOOTH ROADS
 Introduction Introduction
NOTE:
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST R: EXCESSIVE STEERING WHEEL PLAY
PINPOINT TEST R: EXCESSIVE STEERING WHEEL PLAY
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Excessive steering wheel free play is a condition in which there is too much steering wheel movement before the wheels move. The EPAS system is designed to compensate for some steering wheel free play, however a small amount of steering wheel free play is considered normal. Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST M: MESSAGE CENTER DISPLAYS STEERING FAULT SERVICE NOW
PINPOINT TEST M: MESSAGE CENTER DISPLAYS STEERING FAULT SERVICE NOW|
NOTE:
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Possible Sources |
| Diagnostic steps are not provided for this symptom or DTC. REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). |
 PINPOINT TEST BA: STEERING GEAR APPEARS TO BE LEAKING FLUID
PINPOINT TEST BA: STEERING GEAR APPEARS TO BE LEAKING FLUID
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Steering Gears That Appear To Be Leaking Power Steering Fluid
Steering Gears That Appear To Be Leaking Power Steering Fluid Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose External Sources Of Fluids
External Sources Of Fluids Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST BB: B1D23:4B
PINPOINT TEST BB: B1D23:4B
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST BC: U3003:16, U3003:17, OR U3003:68
PINPOINT TEST BC: U3003:16, U3003:17, OR U3003:68
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST BD:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U3001:68
PINPOINT TEST BD:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U3001:68
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST BE:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U3000:4B CONTROL MODULE: OVER TEMPERATURE
PINPOINT TEST BE:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U3000:4B CONTROL MODULE: OVER TEMPERATURE
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST BF:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C1B00 STEERING ANGLE SENSOR - EPAS (ELECTRONIC POWER ASSIST STEERING)
PINPOINT TEST BF:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C1B00 STEERING ANGLE SENSOR - EPAS (ELECTRONIC POWER ASSIST STEERING)

 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST BG:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C200B STEERING SHAFT TORQUE SENSOR 1
PINPOINT TEST BG:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C200B STEERING SHAFT TORQUE SENSOR 1
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST BI:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C200D MOTOR ROTATION ANGLE SENSOR
PINPOINT TEST BI:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C200D MOTOR ROTATION ANGLE SENSOR
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST BK: LACK OF ASSIST OR INCONSISTENT ASSIST
PINPOINT TEST BK: LACK OF ASSIST OR INCONSISTENT ASSIST
 Introduction Introduction
NOTICE: Use the correct probe adapter(s) when making measurements. Failure to use the correct probe adapter(s) may cause damage to the connector. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST BL:
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0420:XX INVALID DATA RECEIVED FROM THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
PINPOINT TEST BL:
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0420:XX INVALID DATA RECEIVED FROM THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)

 Introduction Introduction
NOTICE: Use the correct probe adapter(s) when making measurements. Failure to use the correct probe adapter(s) may cause damage to the connector. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST BO:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U2016 CONTROL MODULE MAIN SOFTWARE
PINPOINT TEST BO:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U2016 CONTROL MODULE MAIN SOFTWARE
 Introduction Introduction
NOTE: When DTC U2016:48 is set, the PSCM remains in normal operation mode, but features such as Active Nibble Control, Pull-Drift Compensation, Lane Departure Warning, Lane Keep Assist, ect. are disabled. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST BQ:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U2100:00
PINPOINT TEST BQ:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U2100:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST Z: MESSAGE CENTER DISPLAYS STEERING LOSS STOP SAFELY
PINPOINT TEST Z: MESSAGE CENTER DISPLAYS STEERING LOSS STOP SAFELY|
NOTE: This message appears when a condition has been detected in the EPAS system requiring the PSCM to disable the system (remove assist) to help prevent the system from sustaining any possible damage. This message (and related symptom) cannot be cleared until the condition is repaired. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Possible Sources |
| Diagnostic steps are not provided for this symptom or DTC. REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). |
 PINPOINT TEST AA:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C1110:56
PINPOINT TEST AA:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
C1110:56
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Description
Description Diagnostic Aid
Diagnostic Aid DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AB:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U2300:55
PINPOINT TEST AB:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U2300:55
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AC: FRONT END NOISE - OVER BUMPS, ROUGH ROADS, DIPS, DEPRESSIONS OR WHEN ENTERING A DRIVEWAY
PINPOINT TEST AC: FRONT END NOISE - OVER BUMPS, ROUGH ROADS, DIPS, DEPRESSIONS OR WHEN ENTERING A DRIVEWAY|
NOTE: Noises over bumps and rough roads involve parts which move and contact during an up and down motion. Possible Sources
|
||||
| AC1 CHECK FOR APPLICABLE SERVICE ARTICLES | ||||
Does a service article exist for any of the above components?
|
||||
| AC2 VERIFY THE NOISE | ||||
Has the noise been verified?
|
||||
| AC3 INSPECTION FOR NOISE SOURCE | ||||
Do any of the listed components appear to be loose, worn, damaged, broken, or impaired?
|
||||
| AC4 VERIFY GENERAL NOISE LOCATION (LEFT OR RIGHT SIDE OF VEHICLE) | ||||
Is the noise louder on the left side?
|
||||
| AC5 EVALUATION FOR LEFT SIDE NOISE | ||||
Do any of the probe locations reveal the noise under consideration?
|
||||
| AC6 EVALUATION FOR RIGHT SIDE NOISE | ||||
Do any of the probe locations reveal the noise under consideration?
|
||||
| AC7 EVALUATION FOR NOISE IN CENTER | ||||
|
NOTE: NOTE: The steering gear is central to steering system and noises may be transferred to it from other nearby components.
Do any of these probes reveal the noise under consideration?
|
||||
| AC8 INSPECT THE STEERING GEAR ATTACHMENT POINTS | ||||
Are the listed components secured correctly and are all fasteners tightened to specifications?
|
 PINPOINT TEST AD: FRONT END NOISE - NOTICED MORE IN THE INTERIOR
PINPOINT TEST AD: FRONT END NOISE - NOTICED MORE IN THE INTERIOR
 Introduction Introduction
NOTE: Interior cabin noises involve parts moving or contacting during a steering wheel turn or interior parts moving or contacting during steering column tilt or telescopic operations. Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AE: FRONT END NOISE - TURNING AT SLOW SPEEDS OR DURING PARKING LOT MANEUVERS
PINPOINT TEST AE: FRONT END NOISE - TURNING AT SLOW SPEEDS OR DURING PARKING LOT MANEUVERS|
NOTE: Exterior front end noises when turning at slow speeds involve parts which move, rotate or make contact during a partial or full turn. Please note whether the vehicle has column mounted EPAS, steering gear mounted EPAS or adaptive steering. Possible Sources
|
||||
| AE1 CHECK FOR APPLICABLE SERVICE ARTICLES | ||||
Does a service article exist for any of the above components?
|
||||
| AE2 VERIFY THE NOISE | ||||
Has the noise been verified?
|
||||
| AE3 INSPECTION FOR NOISE SOURCE | ||||
Do any of the listed components appear to be loose, worn, damaged, broken, or impaired?
|
||||
| AE4 VERIFY GENERAL NOISE LOCATION (LEFT OR RIGHT SIDE OF VEHICLE) | ||||
Is the noise louder on the left side?
|
||||
| AE5 EVALUATION FOR LEFT SIDE NOISE | ||||
Do any of the probe locations reveal the noise under consideration?
|
||||
| AE6 EVALUATION FOR RIGHT SIDE NOISE | ||||
Do any of the probe locations reveal the noise under consideration?
|
||||
| AE7 EVALUATION FOR NOISE IN CENTER | ||||
|
NOTE: NOTE: The steering gear is central to steering system and noises may be transferred to it from other nearby components.
Do any of these probes reveal the noise under consideration?
|
||||
| AE8 INSPECT THE STEERING GEAR ATTACHMENT POINTS | ||||
Are the listed components secured correctly and are all fasteners tightened to specifications?
|
 PINPOINT TEST AF: FRONT END NOISE - DURING ACCELERATION OR DECELERATION MAY OCCUR WITH BRAKING
PINPOINT TEST AF: FRONT END NOISE - DURING ACCELERATION OR DECELERATION MAY OCCUR WITH BRAKING|
NOTE: Noises when accelerating or decelerating involve parts which move during an acceleration tip-in (pressing foot on gas pedal) or parts which move during deceleration tip-out (when taking foot off gas pedal). These noises are not typically associated with the steering gear. Possible Sources
|
||||
| AF1 FRONT END NOISE EVALUATION | ||||
Does the noise ONLY occur during vehicle braking?
|
||||
| AF2 SERVICE BAY ACTIVE UNDER HOOD FRONT END NOISE INSPECTION | ||||
Was the noise identified and located during this test?
|
||||
| AF3 VISUAL INSPECTION FOR FRONT END NOISE SOURCE | ||||
Are all of the listed components OK?
|
 PINPOINT TEST AG:
ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
MODULE DTC C0051 STEERING ANGLE CONCERNS WITH THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
- MECHANICAL
PINPOINT TEST AG:
ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
MODULE DTC C0051 STEERING ANGLE CONCERNS WITH THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
- MECHANICAL
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions The PSCM calculates steering wheel rotation speed, angle and direction of rotation and sends the information to the ABS module over the CAN . If the information is incorrect, invalid or corrupted, the ABS module sets one or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AH:
ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
MODULE DTC C0051 STEERING ANGLE CONCERNS WITH THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
- ELECTRICAL
PINPOINT TEST AH:
ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM)
MODULE DTC C0051 STEERING ANGLE CONCERNS WITH THE PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
- ELECTRICAL
 Introduction Introduction
NOTICE: Use the correct probe adapter(s) when making measurements. Failure to use the correct probe adapter(s) may cause damage to the connector. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AI: FRONT END NOISE - DURING BRAKING
PINPOINT TEST AI: FRONT END NOISE - DURING BRAKING|
NOTE:
Possible Sources
|
||||
| AI1 FRONT END NOISE EVALUATION | ||||
Does the noise ONLY occur during vehicle braking?
|
||||
| AI2 SERVICE BAY ACTIVE UNDER HOOD FRONT END NOISE INSPECTION | ||||
Was the noise identified and located during this test?
|
||||
| AI3 VISUAL INSPECTION FOR FRONT END NOISE SOURCE | ||||
Are all of the listed components OK?
|
 PINPOINT TEST AJ:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0100:00
PINPOINT TEST AJ:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0100:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AK:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0121:00
PINPOINT TEST AK:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0121:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AL:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0140:00
PINPOINT TEST AL:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0140:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AM:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0146:00
PINPOINT TEST AM:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0146:00
 Introduction Introduction
NOTE: The serial data gateway module is also known as the GWM Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AN:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0151:00
PINPOINT TEST AN:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0151:00
 Introduction Introduction
NOTE: Do not install a new PSCM as part of the repair for a PSCM DTC U151:00. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AO:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0155:00
PINPOINT TEST AO:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0155:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AP:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0159:00
PINPOINT TEST AP:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0159:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AQ:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0212:00
PINPOINT TEST AQ:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0212:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AR:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U023A:00
PINPOINT TEST AR:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U023A:00
 Introduction Introduction
NOTE: Do not install a new PSCM as part of the repair for a PSCM DTC U023A:00. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AS:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0401:00
PINPOINT TEST AS:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0401:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AT:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0415:00
PINPOINT TEST AT:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0415:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
Visual Inspection and Pre-checks
|
 PINPOINT TEST AU:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0429:00
PINPOINT TEST AU:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0429:00
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AV:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0447:00
PINPOINT TEST AV:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U0447:00
 Introduction Introduction
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AW:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U045A:00
PINPOINT TEST AW:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U045A:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 PINPOINT TEST AX:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U053B:00
PINPOINT TEST AX:
PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE)
U053B:00
 Introduction Introduction
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 43 for schematic and connector information. Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
REFER to: Power Steering - System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). Description
Description Pinpoint Test Applicability
Pinpoint Test Applicability DTC Diagnostic Strategy
DTC Diagnostic Strategy Pinpoint Test Purpose
Pinpoint Test Purpose Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Aids DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
Possible Sources
|
 Removal and Installation - Steering Gear
Removal and Installation - Steering Gear
Removal
Remove the front subframe.
Refer to: Front Subframe (502-00 Uni-Body, Subframe and Mounting System, Removal and Installation).
Remove and discard the steering gear retainers...
Other information:
Lincoln Corsair 2020-2026 Owners Manual: Side Sensing System
WARNING: The system may not detect objects with surfaces that absorb reflection. Always drive with due care and attention. Failure to take care may result in a crash. WARNING: The system may not detect small or moving objects, particularly those close to the ground...
Lincoln Corsair 2020-2026 Service Manual: Removal and Installation - Steering Column
Removal NOTICE: To prevent damage to the clockspring, make sure the front wheels are in the straight-ahead position. NOTICE: Precise tolerances are required when manufacturing a steering column. Never install a repaired, rebuilt, aftermarket, or remanufactured steering column...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 1st Generation Lincoln Corsair Owners Manual
- 1st Generation Lincoln Corsair Service Manual
- Programming the Garage Door Opener to Your Garage Door Opener Motor
- Selecting a Drive Mode. DRIVE MODES
- Head Up Display
- New on site
- Most important about car
Information on P Type Tires
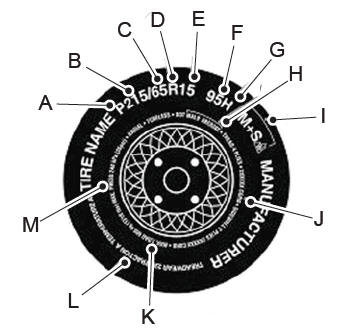
P215/65R15 95H is an example of a tire size, load index and speed rating. The definitions of these items are listed below. (Note that the tire size, load index and speed rating for your vehicle may be different from this example.)
P: Indicates a tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association, that may be used for service on cars, sport utility vehicles, minivans and light trucks. Note: If your tire size does not begin with a letter this may mean it is designated by either the European Tire and Rim Technical Organization or the Japan Tire Manufacturing Association. 215: Indicates the nominal width of the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire. 65: Indicates the aspect ratio which gives the tire's ratio of height to width. R: Indicates a radial type tire. 15: Indicates the wheel or rim diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel diameter. 95: Indicates the tire's load index. It is an index that relates to how much weight a tire can carry. You may find this information in your owner’s manual. If not, contact a local tire dealer.
 PINPOINT TEST A: OPEN PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
FUSE(S)
PINPOINT TEST A: OPEN PSCM (POWER STEERING CONTROL MODULE)
FUSE(S)


 Introduction
Introduction
